- Web-based applications are still very popular, even with the growing popularity of mobile native apps. The main reasons for this are accessibility, consistent performance and design on different devices, and cost efficiency.
- Sometimes, mobile applications offer more advanced functionalities due to access to the device's hardware and storage. However, web apps have shown significant growth and can access a lot of hardware functionalities today, bridging the gap between native and web approaches.
- The cross-platform app development model enables cutting costs without compromising quality and reaching users using different devices and OS.
It’s been a while since the number of Instagram app users exceeded one billion. In the US solely, more than 140 million users have an Instagram account and use either iOS or Android apps to access the service.
At the same time, Instagram is available as a web app via a web browser.
Why would such a booming mobile app need a web version?
Why does Instagram need to support and maintain a website if its mobile application blooms, blossoms, and requires many resources?
Why now, in a mobile-everything era, companies launch web-based applications?
Apparently, there are a number of users that need Instagram in their browsers. And as the company tries to satisfy all the demands, Instagram launched a web version and filled the gap.
Today, you will find out about the companies that extend their businesses with web apps, discover how web apps differ from mobile apps, and decide if you should build a web app for your business.
Web-based application: is it still something businesses go for?
As you may already know, Instagram’s success story started with a location-tagging mobile app. Later, location tagging changed with photo-sharing functionality, but the product was still available for smartphone users only.
More than two years after the app release, in November 2012, Instagram founders decided to extend the horizons and go web.
Here’s what Kevin Systrom, ex-CEO at Instagram, said:
People have been asking for this for a while now. We’re launching web profiles to give you a simple way to share your photos with more people and to make it easier to discover new users on the web.
It was quite a long time ago, though. Now, the Internet industry has drifted to a mobile-first tendency, and the web-app-first age is over.
Or isn’t it?
Telegram, an instant messaging app, was launched for iOS and Android platforms in 2013. In 2014, the unofficial web version saw the world. Users probably wanted to have instant access to their Telegram messages on their laptops, even at work or when they forget their smartphones at home. The Telegram team responded to the expectations and released a web app.
What about some recent news?
Revolut, a FinTech company based in London, has been providing online banking services since 2015. Via a mobile application available on Android and iOS, users can easily monitor their spending, exchange currencies, send money to other accounts, etc. In February 2020, Revolut introduced the web app:
Whatever the reason for wanting to view your account on desktop, now you can. It’s always nice to have the option of both desktop and mobile - and know that your account will always be available to you.
It’s all about a better user experience. As web-based application examples demonstrate, if you implement a multi-channel approach and allow users to access your app on multiple platforms and devices, you have more chances to engage and make them stay with your product. Just think about how often you use GPT-chat, Netflix, Spotify, or Google Docs via web browser.
What should you know about a web-based application? And how does it differ from a mobile solution? Let’s find out.
Web application explained
The major part of modern websites are web apps, and any component of the website that provides service may be qualified as a web app.
We use web applications every day, maybe without even noticing these are actually web apps:
- Webmail services (Microsoft Outlook, Gmail);
- Online calendars (Google Calendar);
- Online calculators (Desmos);
- eCommerce products (Shopify);
- Online marketplaces (Amazon);
- Reviews and rating services (Yelp) etc.

Now, let’s see what a web app is and how it differs from a mobile app.
To use a mobile app, you need to download it from the app store. Mobile apps are built for each specific platform. And there’s no way to download an app available on AppStore only to your Android device.
Web applications work differently. You can use either a good old Blackberry, iPhone 15, or a SmartTV and access a web application via a web-based system and a browser.
Since its launch in 2020, the Clubhouse audio social app was initially available on iOS devices only. Amazingly popular among millions of users worldwide, it was potentially interesting for Android smartphone owners, too. However, there was no chance to access it: in spring 2021, the Clubhouse team only planned to start working on the Android version. As a result, both giants like Meta and small startups focused on web-based app ideas similar to Clubhouse for all popular mobile platforms. The competition got intense. And what about the Clubhouse Android app? They released it too late when the demand decreased. And now we haven’t heard about Clubhouse for a few years anymore.
By launching a web app, you may avoid this trouble. No matter what mobile platform your target audience prefers, anyone can reach it via a browser.
A web app architecture consists of two parts responsible for client-side and server-side rendering:
- User interfaces (app’s front-end) is a part users can see and interact with;
- Server-side (app’s back-end) is responsible for the connection and data exchange with web servers, databases, third-party APIs, etc.
To launch a high-quality web app, you need a strong team of several engineers, each of them skilled in the defined tech stack. If you lack the necessary expertise, consider web development outsourcing services.
Now, let’s find out more about the client and server side of web apps.
Web app’s front-end
UI, or front-end, is a visual representation of a product, such as a web based application design. It’s the part of the app users directly interact with.
Front-end developers work with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript for application development. A vast number of JavaScript frameworks (including Vue React, and Angular) allow to simplify and optimize development, as well as create a sophisticated, interactive web app’s interface.
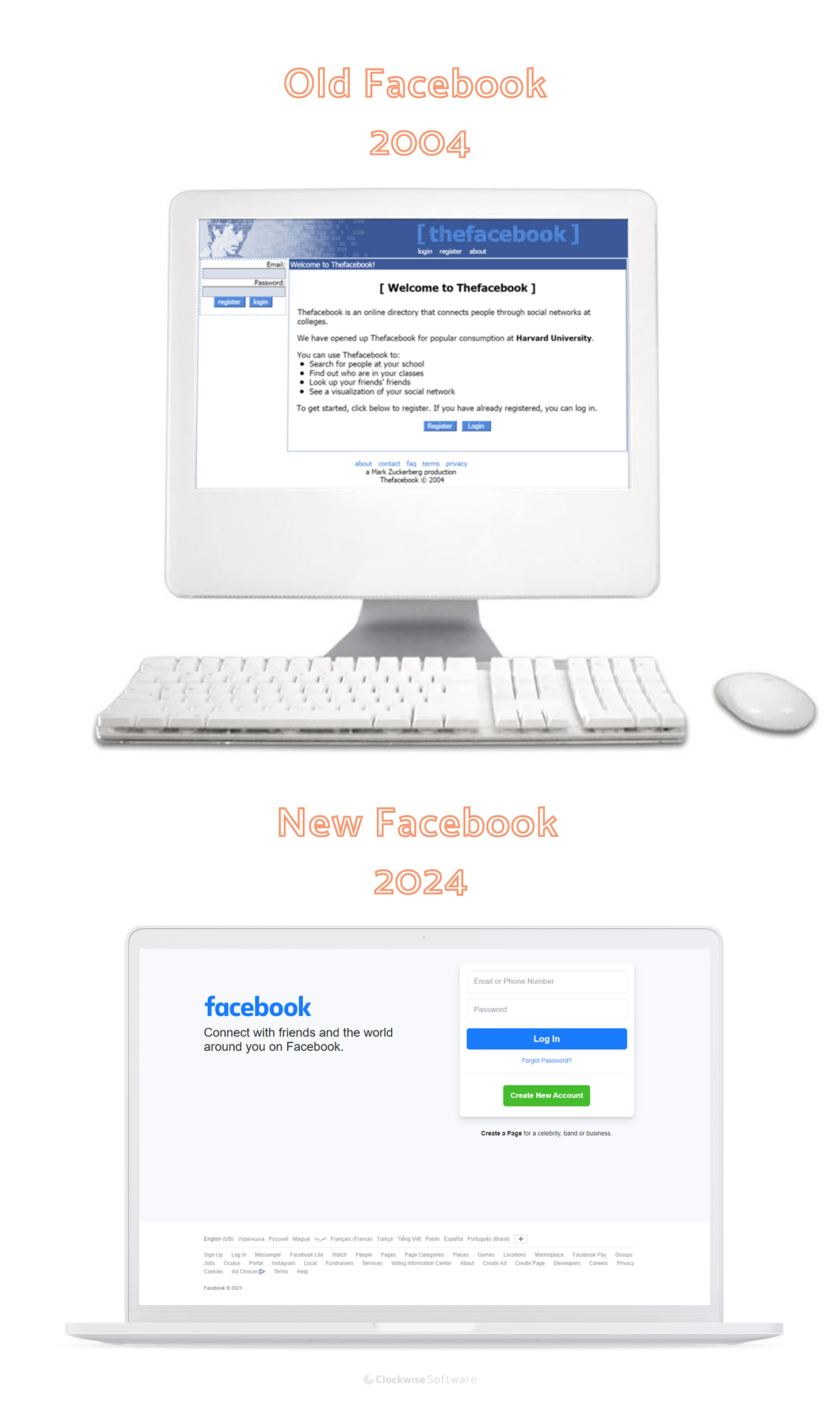
Take a look at Facebook from 2005 and now. Can you see the difference? As the years go by, the web world becomes better as web technologies become stronger. Understanding the latest trends in web design is the key to success in the web app development world.
Web app’s back-end
The back-end is hidden from the user’s eyes. The server-side is a part of the app responsible mainly for processing and storing data.
Back-end engineers can choose from multiple technologies to build the app’s server-side. According to Stackoverflow, JavaScript-based Node.js is the most popular technology for back-end development. PHP, Ruby, Python, Java, and many other programming languages allow building the app’s back-end as well. The choice depends on the web app requirements document and your resources, plans, and expectations.
To better understand how to create a web-based application, compare traditional web apps with web-based SaaS applications. Analyze the advantages and drawbacks of on-premise servers and cloud-based architecture, learn more about how cloud and SaaS models benefit each other, and choose the best approach for your project.
So, what are your web app project requirements? What should you build: a web app or a mobile app? Or maybe both? If you are at a crossroads now, let us help you with the choice.
Web based applications benefits
From a business perspective, web-based application development has multiple advantages. Here are some of them.
No installation required
To visit a web app, you need to take a single step: enter the web app’s URL in the address bar. Another way is to go to Google, enter the website’s name, and click on a link. That’s it. Several seconds keep you away from the information, company, or service you search for.
In the case of a mobile app, the installation process may take up to several minutes. First, users need to go to the app store and find an app there. Then, they start the installation and wait for an app to be downloaded on a device. The app requires the device’s resources, a good Internet connection, and enough memory. App installation may become tedious and time-consuming if the connection is slow or the device’s memory is full. This is why many potential users avoid new apps.
Here’s another case. On vacation, when visiting a new town, users may need to install a local ride-hailing app. But the next day, they may go to another city where this app is useless. It is very likely they don’t want to install a new app just for one ride. And that’s another of web based applications advantages: users can find information or order a service in a matter of seconds without unnecessary installation.
To attract users who’d like to avoid installing new apps, consider creating web based applications for your business.
Multiple users – same version of a product
The problem with Android and iOS apps is frequent updates.
While well-established companies can allocate resources to support the app’s previous versions, startups may find it rather difficult. As soon as a new OS version rolls out, the development team may lack resources to support some of the older versions. Users of older OS versions notice that something went wrong, experience lags, bugs, or other issues, and delete an app.
On a web app, there are no such problems. No matter how often the team updates the product, all users across all platforms can see the same result and can use the latest web based application’s version. It simplifies management and support: the team doesn’t have to worry about users unable to update an app. There’s no need to send personalized notifications or emails to remind users of upcoming updates.
Multiple users – same functionality and design
Native apps on Android and iOS may look and work differently. Different system requirements, different development approaches, and technologies, drop by drop, contribute to the vivid contrast of designs. Starting from minimum tap target size to lists, navigations, and CTAs, apps may look different.
Switching from an Android to an iOS device or vice versa, mobile app users may experience inconvenience or notice some new screen elements. In the case of customized web applications, it is not going to happen.
Web applications may have constraints, but they look the same for all users.
Cost efficiency
Another critical factor to keep in mind is web app cost efficiency.
- If you are up to build custom web-based applications, you pay for a single, cross-platform, cross-browser solution.
- If you want to develop a native mobile app and target both Android and iOS users, you need to build two separate apps and pay double the price for development services.
For a self-funded startup or the one in a pre-seed investment stage, native mobile app development may be a terrible budget eater. Even efficient ways to save money without sacrificing quality, such as outsourcing software development in Ukraine, won’t be able to cover for the native app’s significant costs.
However, if mobile app development is critical for your business, we have a cure. Check the bonus section at the end of the article.
Web based applications disadvantages
Although it may seem like a web application is one-fits-all-solution, it is not quite like this. Along with benefits, many limitations emerge. Take a look at the most serious ones:
Access to native hardware
Just a few years ago, you couldn’t access your device’s storage or hardware features if you opened traditional web apps in a browser. Now you can record a live video or audio with a laptop or a PC, although NFC or geolocation still work better in native apps.
However, in recent years, we have witnessed an emergence of progressive web apps (PWAs). They offer native-like performance without the need for installation, taking full advantage of the user's device hardware and storage. PWA can run offline and send push notifications. Progressive web apps are not replacing native anytime soon due to limited functionalities and lack of hardware and software support. But we still recommend consulting with your software development or IT outsourcing partner and consider building PWA.
Thus, if your app requires access to hardware features, study the capabilities of modern frameworks before choosing or denying web app development.
Promotion challenge
An app deployed on Play Market or App Store gets a powerful promotion channel: a digital distribution platform. Play markets allow users to quickly find applications they may look for. Intuitive search bar, filters, and categories increase your app’s chances to be noticed. The higher the rating your app will have - the more often it will be shown to an interested audience.
Users looking for your app, may go to play markets directly. When they don’t find your app there, they download an alternative instead.
Building a web app, you need to think about its promotion and monetization thoroughly, as in comparison to a mobile app, you lose a solid promotion channel.
When a web-based application is not a good choice
The web-based application won’t serve your business needs effectively if you plan to build:
- Location-tagging apps like Foursquare;
- Delivery and shipping apps;
- Navigation apps;
- Social video sharing apps like TikTok;
- Real-time photo-sharing apps etc.
Web applications vs. mobile applications
Now, let’s analyze several decisive factors:
| Web app | Mobile app | |
| Content consumption vs content production | More suitable for content consumption | More suitable for content creation |
| User experience | Limited access to the native OS features | Seamless integrations and access to the device’s hardware and OS |
| Updates | Painless and unnoticeable | Requires installation |
| Performance | Depends on the speed of Internet connection and web browser | App’s performance depends on the smartphone’s capabilities |
| Development | Faster as developers work on a single app that runs in any browser | Requires specific technologies and development approach. In a case with native development, requires two separate teams to work on Android and iOS apps |
| Profitability and promotion | A well-planned promotion strategy is required | Clear promotion and monetization strategy via app stores |
| Cost | Requires less investments | Requires more investments |
Bonus section: Two apps with one shot, or how to build both mobile and web apps simultaneously
The best way to meet potential users’ needs, solve existing problems and provide value is to make your app available as a web app and a mobile app at the same time.
Earlier, we’ve mentioned that it may be expensive to build two separate apps for Android and iOS. Add a price for a web-based app – and the budget may jump to hundreds of thousands of dollars.
But there’s a way to cut costs without losing quality.
You can build a cross-platform product using hybrid technologies. In this case, you get several applications: an app available all across the Web as a web application, and a mobile product available as Android and iOS mobile applications on App Store and Play Market.
Cross-platform app development means using specific frameworks. Software engineers build an app’s core – a large reusable piece of code, and then wrap it with different small components to make it specifically a web, Android, or iOS app. Depending on the app’s features, engineers may need to add some native modules created specifically for Android or iOS. Cross-platform apps have access to the native operating system, so the performance doesn’t suffer.
There are two types of cross-platform app development:
- Hybrid app development using Ionic software development kit or Cordova framework;
- Native cross-platform app development using React Native JS framework or Flutter - software development kit built by Google. To choose between Cordova and React Native, consult with your software development partner.
When to choose hybrid app development vs. native cross-platform app development? Check our article about cross-platform apps to make time and a cost-effective decision.
In conclusion
To open a web app, users need a good Internet connection and a browser. A web app is a fast and straightforward solution to inform users about your brand, sell products or services online, interact with customers, and let them communicate on your platform, etc. With the emergence of single-page applications, progressive web apps, and more dynamic websites, modern web applications capabilities only continue to grow.
At the same time, even progressive web apps can’t access many of smartphone’s resources. Thus, if you plan to build an app around photo-and video-sharing functionality, GPS, or NFC, consider other options, like native development, cross-platform or hybrid development.
If you would like to find out more about the web, mobile or cross-platform development, its time, and price, just drop us a line.


