AI solutions
What we do
Services
Experts in
How we work
On the way to your organization’s growth, when facing new challenges and looking for a cloud solution to overcome them, you might have come across information about the three common types of cloud computing services:
Indeed, SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS have become the ultimate choice for businesses of different sizes across various industries. They bring convenience to businesses, contribute to easy collaboration, improve business agility, and overall support teams’ productivity.
How does cloud computing bring so many benefits to businesses? What needs can SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS cover for you? How do they differ? You can find the answers in this article.
Looking for the best cloud computing offering that would solve all your problems, you may try to compare SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS. However, we find it not the best way to understand the cloud computing landscape.
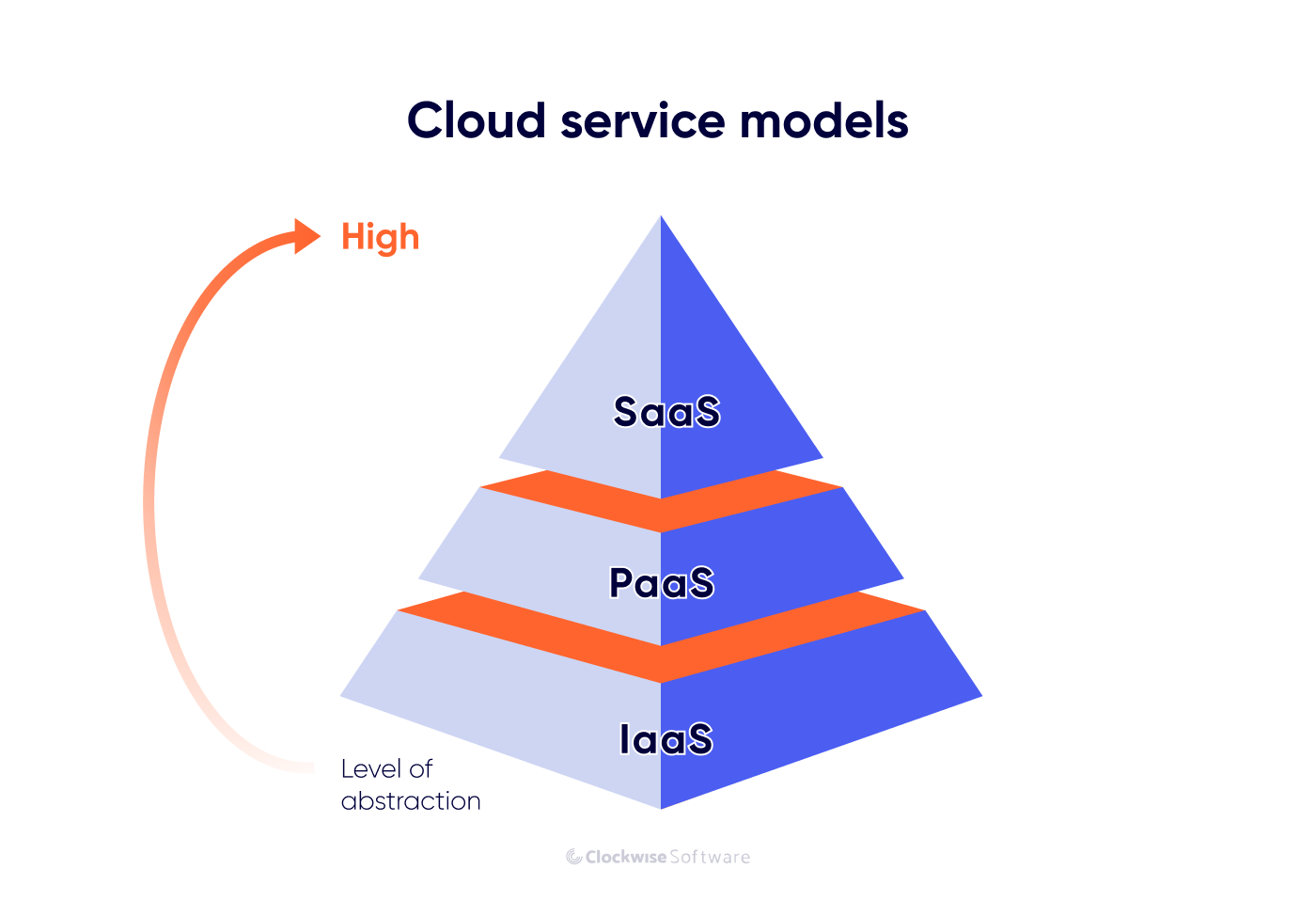
Although SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are parts of cloud computing, it doesn’t mean you can apply any of them to the same problems. They are technologies of different levels that will help you cover different needs to achieve your core business goals. Sounds confusing? Let us explain how it works.
SaaS
When opting for SaaS application development services, you receive a ready-made solution tailored to your specific requirements. For example, it can be a CRM platform that you configure with your data and can effectively manage your sales. This way, you cover your need for a full-featured CRM system without developing and maintaining it.
PaaS
When choosing PaaS, you get a platform with the tools, services, and frameworks required to build an app. This way, you cover your need for a platform to develop, test, and run apps.
IaaS
When choosing IaaS, you can create a development platform using virtualized infrastructure resources like servers, storage, and networking. This way, you can cover your need for an affordable way to host your app without managing physical infrastructure.
As you can see, each offering helps with different problems and can’t replace one another. Instead, they will complement each other within your business ecosystem, offering you a powerful set of tools and services for diverse business needs. That’s why companies typically don’t choose between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS but use each service in appropriate cases.
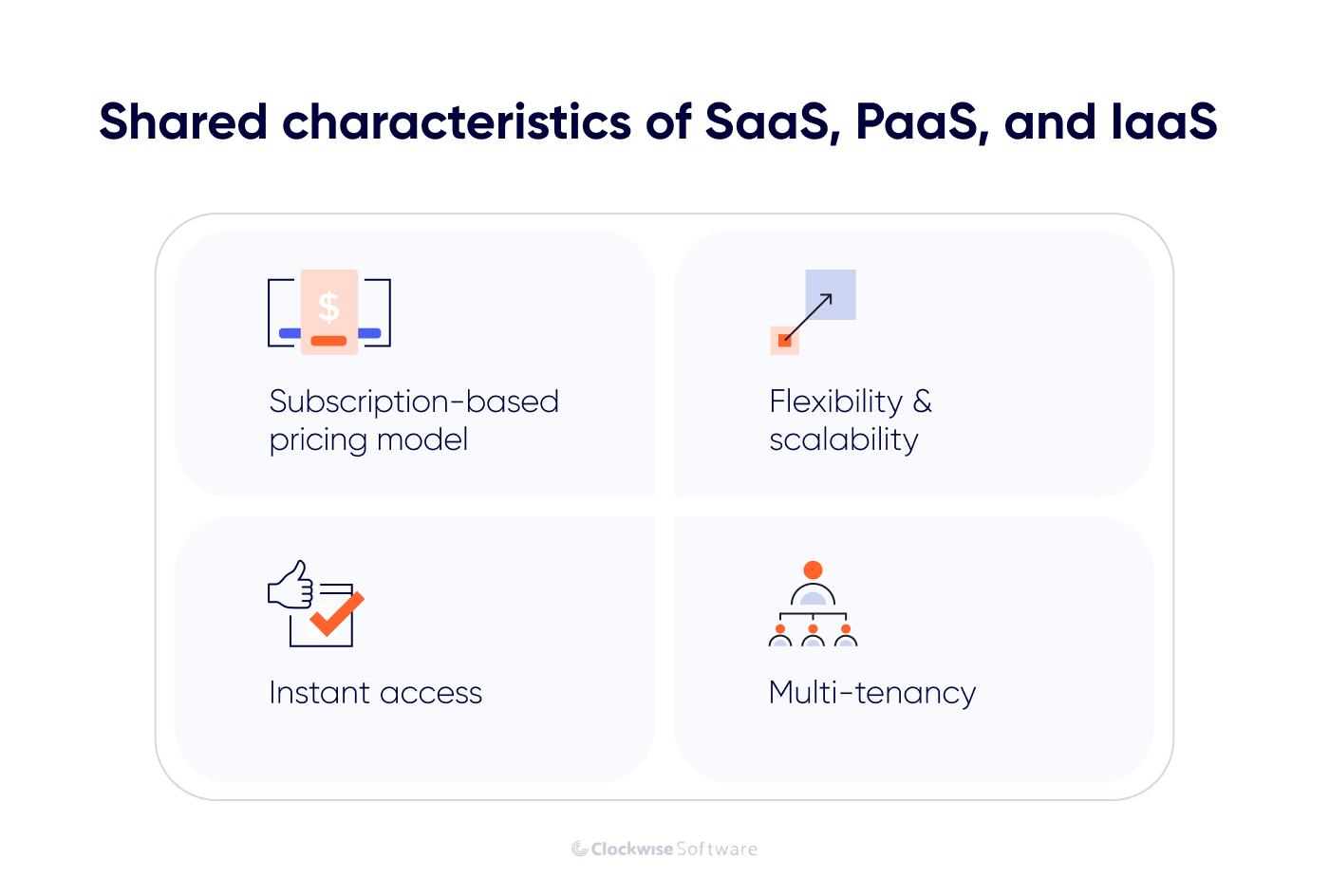
Before explaining the difference between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, we want to outline their common characteristics. After all, there is a reason why people think that these types of services can replace one another, even though this point is misleading.
Besides all these services being part of cloud computing, they have another shared characteristic: the “as a service” part in their names. It means computing resources, platforms, and software are delivered on demand. You don’t buy a cloud solution but rather buy access to it on a subscription basis.
Think of it as Netflix: for a fee, you get access to a library with tons of movies and TV series you can watch without buying each one individually — the same way the “as a service” model works. You access computing resources, platforms, and software you need for your business without owning and managing it locally.
So, here are the characteristics the as-a-service cloud solutions share:
Nevertheless, the fact SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS share a few characteristics doesn’t mean they are interchangeable. Each type of service has its specific use cases. How can you understand when to use IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS? To find an answer, you need to know more about each offering. Let’s start with software as a service.
We are sure you have heard the term “software as a service“ at least once. SaaS refers to the model software delivered to users: on demand for a fixed fee per a certain period (month, year, etc.), per user, or per used resources. With SaaS products, users get all the benefits of the “as a service” model: flexible pricing, excellent scalability, and instant access from any location.
Typically, we perceive cloud and SaaS as interconnected concepts, as most software provided as a service is hosted on the cloud. However, sometimes, on-premises software can also use SaaS as a business model, which means you use a solution on a subscription basis but need to install it on your hardware.
Numerous successful SaaS startups appear every year. In recent years, we saw the launch of Copy.AI, Forecastr, Phyllo, Puzzle, and many other SaaS products for businesses.
Some of the widely known SaaS products are Slack, Mailchimp, and Google Drive. But there are many more, from project management software like Asana and CRM platforms like Salesforce to AI SaaS products like SymphonyAI.
What distinguishes SaaS from on-premises software? The answer is SaaS application architecture.
Software is hosted in the cloud, so it’s possible to access software via a browser. As we mentioned earlier, sometimes you may need to install software on the device you’d like to access it from. In this case, a core functionality may be available even if you don’t have an internet connection. But, to use the app’s cloud storage, receive updates, or access resources hosted on the cloud, you need an internet connection.
Also, most providers use a multi-tenancy model, which means that clients use the same software but are logically isolated from one another, so they don’t have access to each other’s data. And finally, users can access different amounts of features, memory, and other resources, based on their needs. If you want to learn more about the architecture of SaaS products, look at our SaaS architecture white paper.
Now, let’s take a look at the advantages you get with SaaS:
Among other SaaS advantages, we can highlight its flexibility. You can choose what services, features, or resources to pay for, and don’t waste money on what you don’t need.
SaaS apps also have some limitations that can be critical for businesses:
For some businesses, lack of control over their software can be a critical disadvantage. In this case, your best choice may be to build a custom cloud-based application, where you will have control over your app functionality and performance. Additionally, you can turn your custom solution into a SaaS product and get additional revenue by providing it to other businesses.
An example of the switch from using third-party services to owning a SaaS product is our SaaS platform development case. Our client decided to build a custom platform for backing up data from services like GitHub and Trello, as the off-the-shelf software they were using hadn’t met their business needs. We assisted our client on each stage of product development, from choosing a technology stack for a SaaS product and prioritizing features and integrations to developing frontend and backend and launching the SaaS product. We also continue to maintain the released product to prepare for its launch in the new markets.
Catering to different needs, a SaaS product can become an effective solution for businesses of different sizes across various industries. This cloud computing service requires less technical knowledge and effort from companies to implement it than on-premises software, eliminating the need for a large team of IT specialists and significantly reducing implementation and maintenance costs.
SaaS is your option if you’re looking for a solution that will perform well with minimal input from you. By opting for software as a service, you don’t need to worry about its maintenance or upgrade. Also, implementing SaaS into your business workflow is quick, so it’s a perfect fit for businesses with urgent needs.
Platform as a service is a more specific cloud computing offering than SaaS. By choosing this service, you gain access to a platform for building, testing, deploying, and running applications.
As you can understand, you can’t directly cover any of your business needs with PaaS. But, with this type of cloud computing service, you can build software solutions tailored to your needs. The main purpose of this service is to accelerate software development, making it convenient for your team to work on your software throughout all phases of the development lifecycle and giving your organization more control over the app’s security, functionality, and performance.
What can we say about its difference from SaaS? Comparing platform as a service vs software as a service, you can think of PaaS as a lower level of cloud computing: you use it to build cloud-based software that can then be used for business needs. But in this situation, you pay not for access to a ready-made app but for access to tools and environment to build this app.
Widely known PaaS services are Microsoft Azure App Service, Google App Engine, and AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
PaaS platforms come to users equipped with everything needed for app development. You get access to environments, middleware, web and application servers, languages, frameworks, operating systems, databases, and runtimes that you can configure to certain limits. As a result, users can enjoy the following advantages:
At the same time, PaaS is not an ideal solution, and it comes with some limitations:
As we mentioned earlier, the developers are the target audience of PaaS platforms. Integrated tools and environments for developing, testing, and deployment offered by PaaS help a team improve productivity and embrace agile development practices.
However, PaaS is also beneficial for entire organizations, not just developers. Businesses and startups that need to build applications but are not ready to invest time, money, and effort in infrastructure management may find PaaS the ultimate cloud service.
Another situation when businesses can significantly benefit from PaaS is changing demand. Let’s take e-commerce websites as an example. During holidays, they can meet an increased demand, but after holidays the workload usually drops back to the initial level. With PaaS, e-commerce companies can benefit from automatically scaling for the holiday period and scaling down when the workload decreases.
On-demand platforms are also helpful for companies that are going through digital transformation. For example, suppose your organization is moving from on-premises software to cloud-native. In that case, you can choose a platform as a service model for SaaS migration and build a custom cloud-based application.
What if you want to build a cloud-native app, but your organization needs more control over used infrastructure resources? PaaS won’t provide you with this opportunity, but IaaS, the lower-level cloud computing service, can.
With infrastructure as a service, you get all the fundamental resources you need to create an infrastructure and build a cloud-based app: servers, storage capacities, and networking resources. At the same time, IaaS allows you to eliminate the need to manage and maintain physical hardware. Thus, comparing infrastructure as a service vs platform as a service, we can say that IaaS offers much more flexibility and scalability while staying cost-effective as you don’t need to purchase, set up, and maintain servers or a whole data center.
Some examples of IaaS providers are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, DigitalOcean, and Linode.
As you may understand, IaaS providers have much to offer to users. With this cloud solution, you control not only your app functionality but also the environment where you build it and the virtualized infrastructure resources you use to host and run it. Among the main advantages of this offering, we can highlight the following:
However, depending on the business, some advantages — for example, high customization and management of infrastructure resources — can become disadvantages. Managing and maintaining infrastructure is a task that requires solid technical expertise from your team. Otherwise, IaaS can become a burden for your organization and will lead to issues with your app performance. That’s why you must carefully consider your capabilities to manage infrastructure resources before choosing IaaS.
The main category of businesses that should opt for IaaS is large companies with in-house technical teams looking for a flexible and customizable solution. Understanding the limitations of off-the-shelf solutions and having enough specialists to manage their custom product, they may find IaaS a perfect service to overcome those limitations and get more control over the solutions they use for business.
Companies with disruptive applications also usually opt for IaaS. This offering provides them with more flexibility in terms of managing their app functionality, performance, availability, and security.
All in all, IaaS is a leading cloud computing service in terms of scalability and customization. So, if the ability to scale is your primary need, IaaS is your optimal solution.
Now that you know about each cloud service offering, it’s time to sum up everything we shared above and compare SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS. Each offer has its use cases, benefits, and limitations:
So, the main difference lies in what you can manage as a client and what your cloud provider is responsible for. With SaaS, you don’t need to care about how your software is built and what resources are required for it to work well. You just use it to accomplish some tasks. But when using PaaS and SaaS, you care about those details, as you’re the one who builds the software and impacts its functionality and performance.
Answering the question What is SaaS/ PaaS/ IaaS in cloud computing? is just the first step that will help you choose a cloud service offering. Next, you need to understand what offering is the most useful for your specific case. What challenges do you want to overcome with cloud solutions? Do you want to move your services to the cloud or look for an efficient cloud-based app for specific business operations? Are you thinking of creating your own SaaS product to monetize your services?
There are numerous ways you can apply cloud computing to your business. However, if you choose to build a custom cloud-based product or migrate to SaaS, make sure you have a team of technical specialists who know how to work with such services and can develop, manage, and maintain a product for your business.
If you don’t have an in-house team, you can contact us. We are a SaaS software development company with over ten years of experience building cloud-based solutions. We are fluent in the best practices and trends in SaaS development and can build software from scratch with a focus on your core needs and business goals.