AI solutions
What we do
Services
Experts in
How we work
You’ve probably noticed how AI quietly slipped into almost everything we use. From Netflix knowing what you’ll like next to tools that turn a few words into full articles or designs. What started with ChatGPT back in 2022 has now evolved into a whole ecosystem of LLMs and smart AI frameworks that keep pushing what’s possible in tech.
But with so many AI frameworks out there, it’s tough to know which one works best for your project. The right choice depends on what you’re building, your team’s skills, and how far you plan to scale.
That’s exactly why our AI product development company made this guide. You’ll get an up-to-date overview of the top AI frameworks for 2026, complete with use cases, pros and cons, and expert insight from developers who’ve built AI-powered products in the real world. Think of it as your shortcut to picking the right AI framework for your goals, backed by years of hands-on experience from our tech team.
An AI framework is a software environment that gives your team pre-built components for working with models and algorithms. Developers can use it to handle data pipelines, model training, validation, and deployment — all through a clear programming interface.
If you’re planning to add AI to your product, for example, to improve recommendations, automate text processing, or analyze data, you don’t need to start from zero.
So, if you’re planning to add AI to your product, for example, to improve recommendations, automate text processing, or analyze data, you don’t need to start from zero. Here’s why teams rely on AI frameworks:
Ready-made infrastructure. AI Frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch handle low-level math, optimization, and GPU acceleration so your team can focus on model design and performance.
Consistent development. Shared standards across the AI framework help developers write cleaner, more maintainable code and collaborate smoothly on complex projects.
Resource efficiency. Using pretested modules shortens development time and reduces costs compared to custom solutions.
Community expertise. Large open-source communities contribute tutorials, extensions, and pretrained models, making it easier to find solutions or experiment with new ideas.
| Feature | How it helps |
| Simplicity | Frameworks abstract complex operations, letting developers focus on model logic instead of manual calculations. |
| Performance | Optimized to use GPUs or TPUs for faster training and inference. |
| Flexibility | Allow configuration of model layers, loss functions, and optimization algorithms to match your task. |
| Compatibility | Integrate easily with languages like Python, JavaScript, or C++, and connect with other AI frameworks or APIs. |
| Scalability | Suitable for both small-scale tasks and enterprise-level workloads. |
| Model libraries | Include pretrained models for tasks like image recognition, text classification, and speech processing. |
| Interoperability | Many AI frameworks support shared file formats and conversion tools, so you can combine different environments in one pipeline. |
| Active ecosystem | Documentation, updates, and add-ons from the community speed up development and troubleshooting. |
In short, an AI framework is a tested foundation for building smart, scalable systems. It lets your team focus on what matters most, solving real problems and delivering reliable AI features to your users.
Artificial intelligence frameworks aren’t all built for the same purpose. Some are great for designing deep learning models from the ground up. Others focus on making large language models work smoothly inside real-world apps. And a few are built for companies that want to manage and scale AI across entire teams.
To make your choice easier, we’ve grouped AI frameworks by their main job-to-be-done, the kind of task they help your team complete most efficiently.
| Category | Main purpose | Best for |
| Deep learning frameworks | Build and train custom neural networks from scratch. | Teams creating predictive models, vision systems, or NLP tools. |
| LLM orchestration frameworks | Integrate and manage large language models in apps. | Teams developing chatbots, AI assistants, or RAG (retrieval-augmented generation) systems. |
| Enterprise AI toolkits | Scale AI adoption with infrastructure, compliance, and monitoring tools. | Mid-sized and enterprise teams deploying multiple AI products. |
Each category solves a specific challenge in AI product development, from research and prototyping to large-scale deployment. Let’s take a closer look at each type and explore which AI frameworks stand out in 2026.
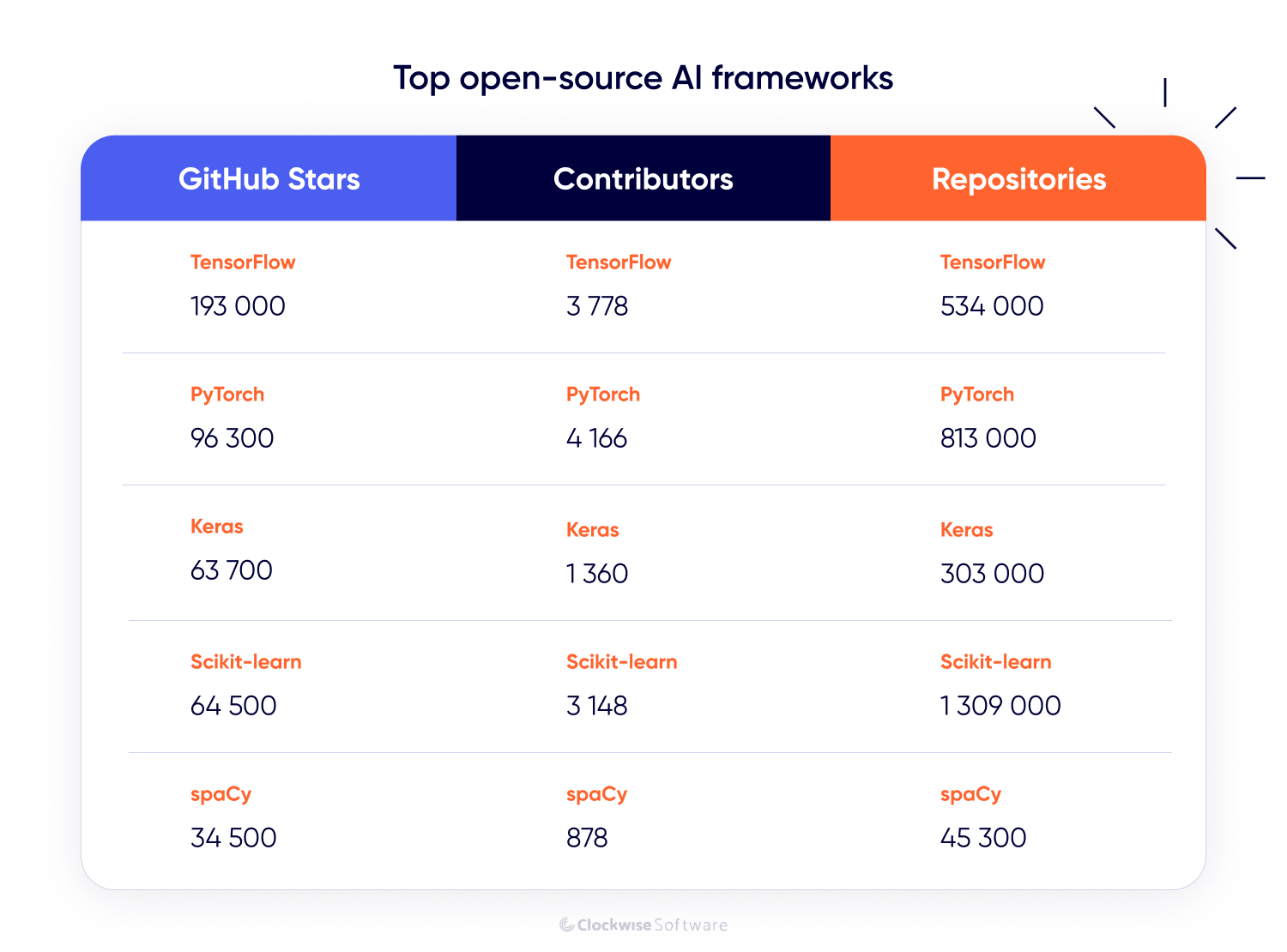
There are dozens of open-source AI frameworks out there, but only a few have become true industry standards. Based on our team’s hands-on experience and data from GitHub and Google Trends, we’ve selected the 5 most widely used frameworks: TensorFlow, PyTorch, Keras, scikit-learn, and JAX. To make this list, we:
Drew on insights from our AI engineers and their project experience.
Reviewed GitHub data, including stars, contributor counts, and active repositories.
Checked Google Trends to track the most searched and discussed AI frameworks over the past year.
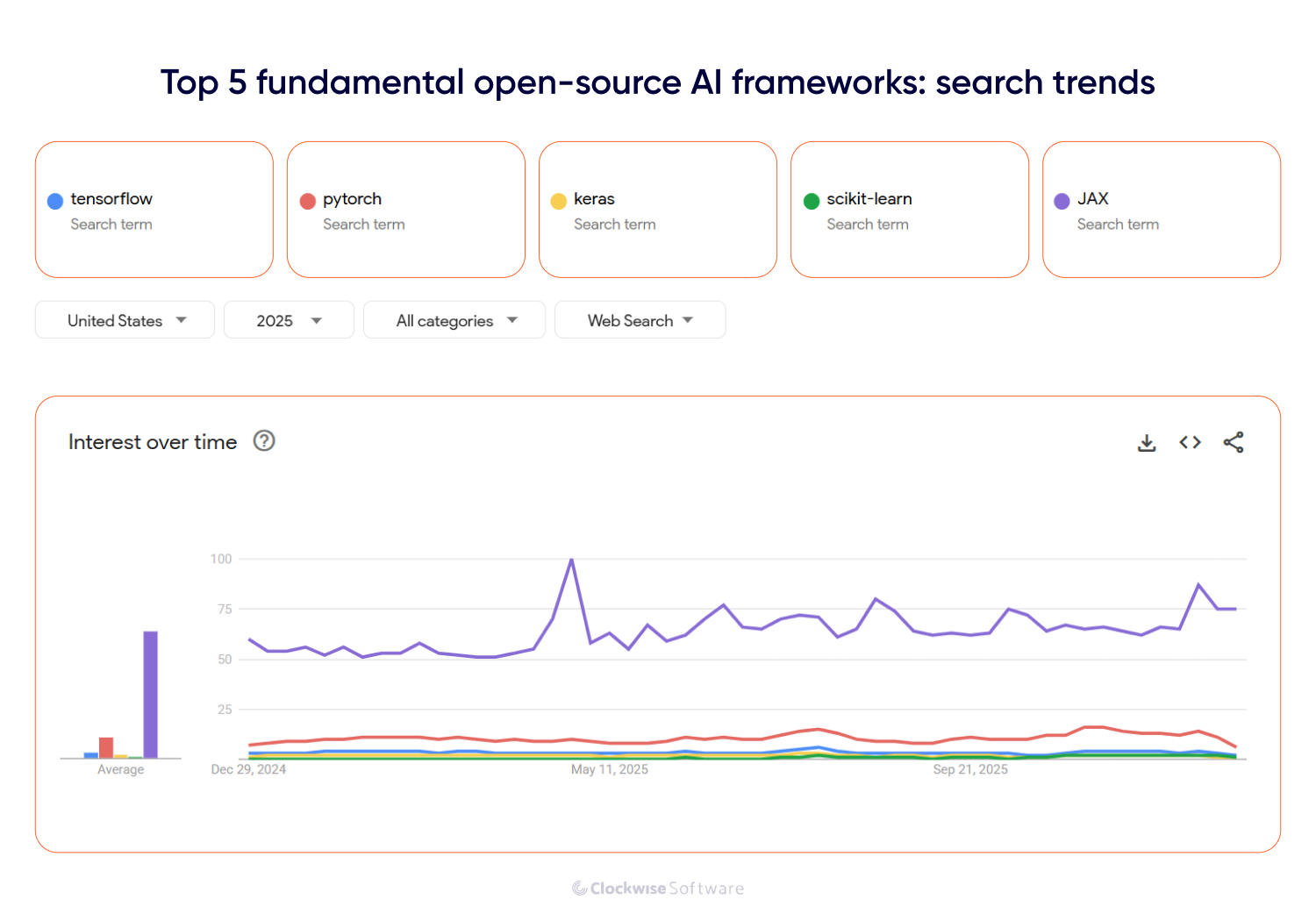
Below, you’ll get to know each AI framework, explore real products built with them, and see where each one shines (and where it doesn’t).
TensorFlow is a powerful open-source machine learning framework developed by Google. Written in Python, it’s built for both training and prediction tasks using neural networks. TensorFlow relies on data flow graphs, which make it possible to design and train deep models that run efficiently across CPUs, GPUs, or TPUs, often without changing a single line of code.
What products benefit from TensorFlow? Since its release in 2015, TensorFlow has powered products across healthcare, social media, and eCommerce. For example, Airbnb uses TensorFlow for image classification, and Google employs it across many of its AI-driven services. You may use TensorFlow to:
As for limitations, TensorFlow can feel heavy for small projects and has a steeper learning curve than some alternatives. It’s best to explore its potential through a PoC before full rollout. It also contains many advanced modules that can be overwhelming for new developers.
Developed by Meta’s AI Research Lab, PyTorch is TensorFlow’s main rival, flexible, intuitive, and designed for experimentation. Its dynamic computation graph allows developers to modify models on the fly, which makes it especially popular in academic and R&D environments. One standout feature is data parallelism, the ability to distribute computations across multiple CPUs or GPUs, boosting training efficiency.
PyTorch is used across diverse industries, from Tesla’s self-driving systems to Instagram’s mobile AI features and Stanford University’s research projects. You can use PyTorch to:
Prototype new models quickly
Develop NLP applications or recommendation engines
Build systems that rely on high-performance parallel processing
While PyTorch is easier to learn than TensorFlow, it has a smaller ecosystem and fewer enterprise-grade tools for deployment. Still, it’s one of the best AI frameworks for teams focused on experimentation and fast iteration.
Keras is a lightweight, open-source AI framework that simplifies deep learning development. Acting as a high-level API (often on top of TensorFlow), Keras helps developers build and train models faster, with less code and cleaner syntax. It’s known for being developer-friendly: good documentation, clear error messages, and minimal configuration make it great for teams starting their AI journey.
Keras is a popular option for image and object recognition, NLP, and predictive analytics. Organizations such as NASA, YouTube, and Waymo use Keras in their deep learning workflows, showing that it’s reliable enough for both rapid prototyping and production-grade AI tasks. Keras is useful for:
Extending an existing TensorFlow-based model
Testing new architectures and tune hyperparameters
Simplifying onboarding for new developers
Keras depends on a backend (usually TensorFlow), so its flexibility and performance are tied to that ecosystem. It’s less suited for highly customized research projects, and its community is smaller than those of TensorFlow or PyTorch.
scikit-learn is a classic in the machine learning world. Written in Python and partly in Cython (a faster variant of Python), this AI framework is designed for predictive data analysis rather than deep learning. It integrates tightly with other scientific libraries such as NumPy, SciPy, and Matplotlib, giving developers everything they need for statistical modeling and visualization. You’ll find scikit-learn behind many data-driven tools, including Spotify’s music recommendation system. It’s ideal for projects involving classification, clustering, and predictive analytics. Here’s what you can do with scikit-learn:
Start exploring machine learning as a beginner
Add fraud detection or churn prediction features
Build models for recommendation or sentiment analysis
It is worth mentioning that scikit-learn doesn’t handle heavy deep learning tasks or massive datasets efficiently. It’s best suited for small to mid-size projects and structured data analysis.
Developed by Google, JAX is a relatively new artificial intelligence framework designed for high-performance numerical computing and automatic differentiation. It combines the simplicity of NumPy with GPU and TPU acceleration, making it a strong choice for cutting-edge research and optimization-heavy workloads. JAX is often used in research environments, reinforcement learning, and large-scale model training. It’s a favorite among teams exploring next-generation architectures, including some of the work behind Google DeepMind projects. You may use JAX to:
Build custom algorithms with automatic differentiation
Run large-scale experiments on GPUs or TPUs
Accelerate deep learning research with flexible computation graphs
The ecosystem around JAX is still growing. It’s less suited for plug-and-play AI app development and more for teams doing advanced model experimentation or custom optimization work.
Each of these AI frameworks brings something different to the table, from TensorFlow’s enterprise scalability to JAX’s research-grade performance. Together, they cover everything from classic machine learning to state-of-the-art deep learning, giving developers the flexibility to choose the right foundation for their next AI product.
LLM integration can transform your product, from automating content creation and data analysis to powering conversational interfaces and intelligent assistants.
LLM orchestration frameworks simplify how developers build, connect, and deploy LLM-powered applications. They help manage context, prompts, and data retrieval, ensuring your language model performs reliably at scale.
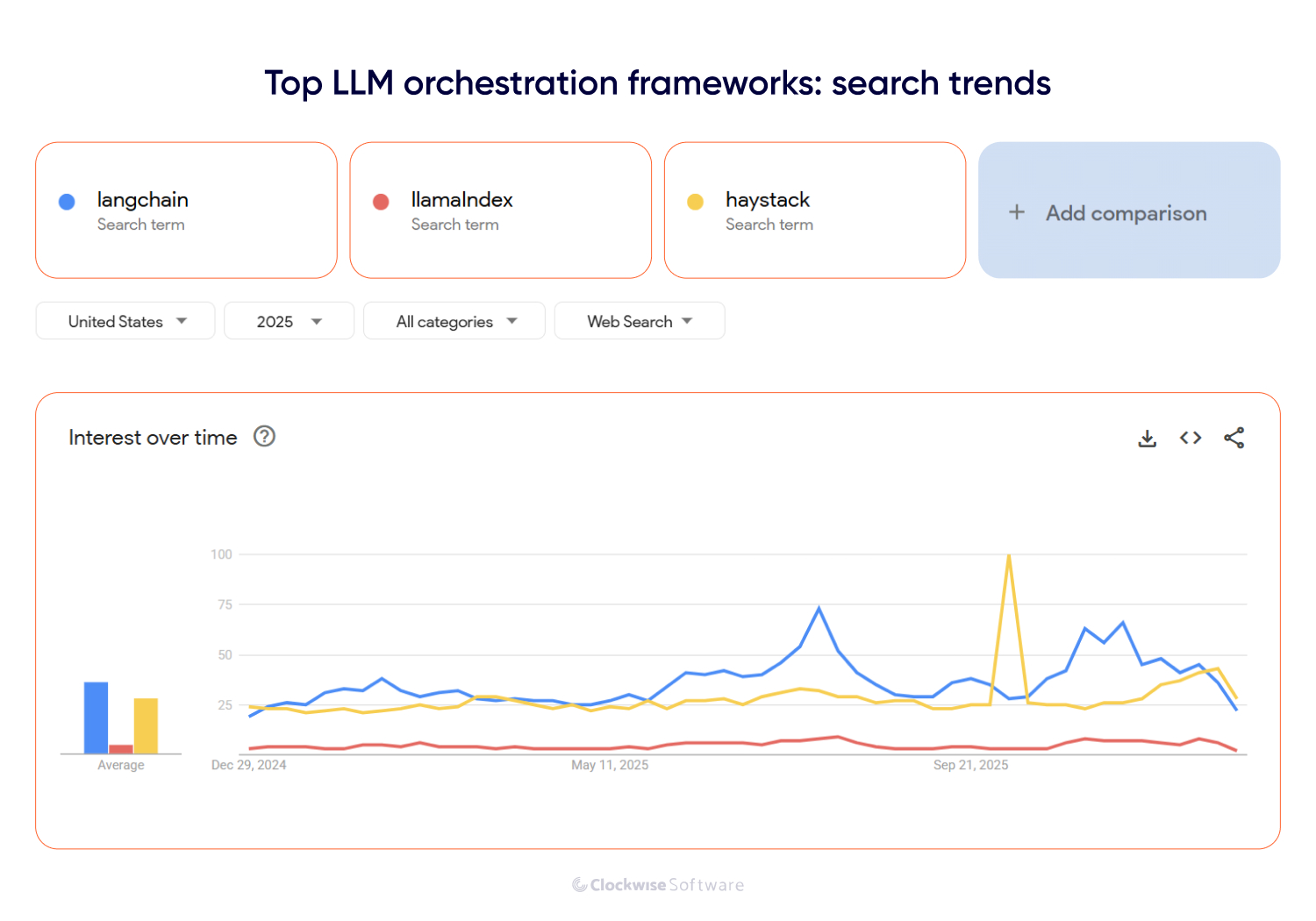
Below, we review 3 of the most popular orchestration frameworks used in 2025.
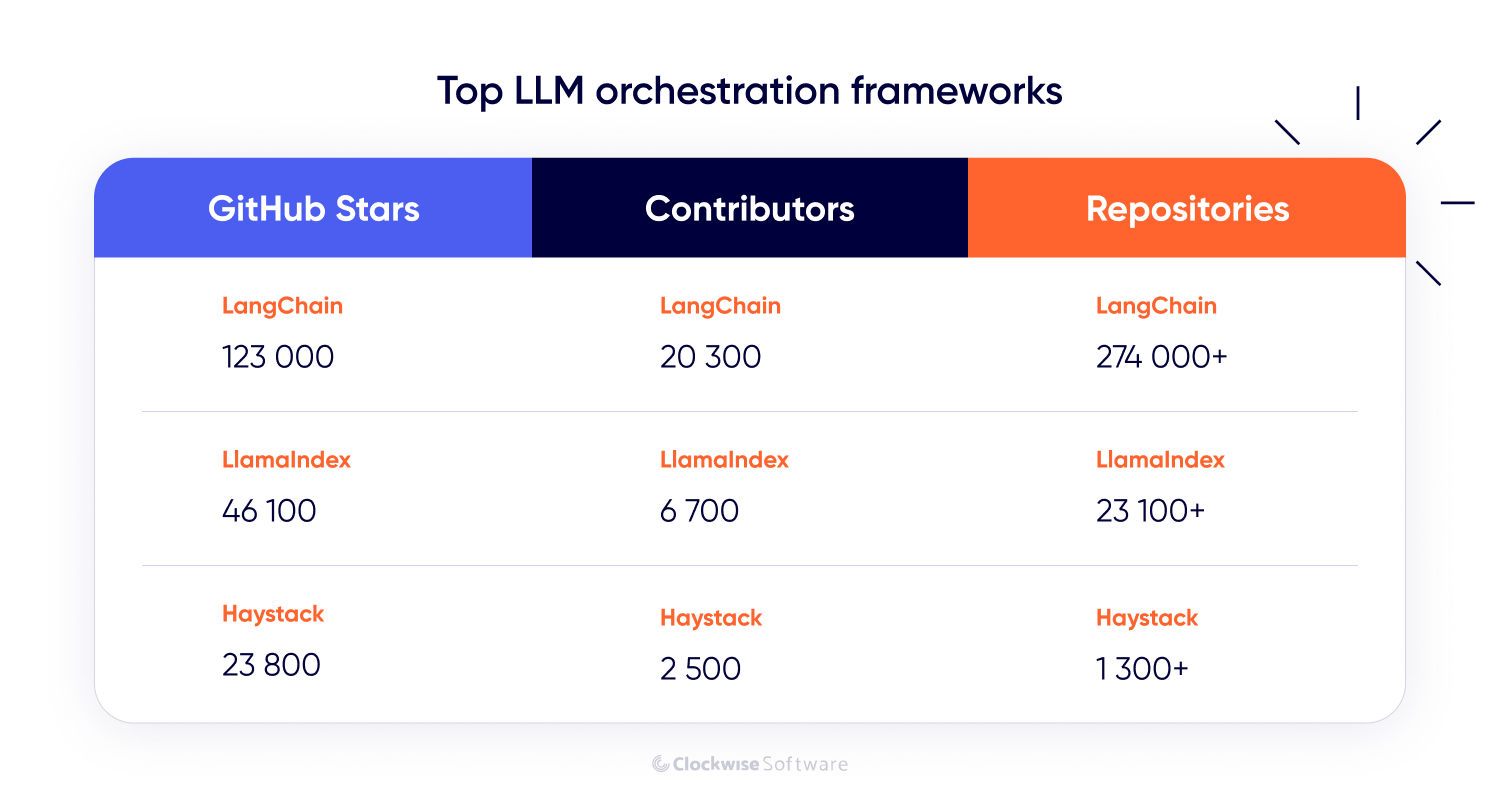
LangChain is one of the most widely used open-source AI frameworks for building applications around large language models. It helps you connect an LLM with your own data and APIs, design reasoning chains, and create autonomous agents capable of decision-making and problem-solving.
LangChain’s library includes prebuilt components and templates that make it easier to develop chatbots, personal assistants, or code-understanding tools. It also integrates with major cloud providers, AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure, making it suitable for both startups and large enterprises.
Companies like Instacart, Zapier, Dropbox, and Adyen use LangChain to enhance support tools, automate operations, and personalize customer experiences. Many tech startups adopt it to build internal AI copilots or customer-facing assistants. LangChain’s great for tasks like:
Developing AI agents that make independent decisions
Creating virtual assistants and chatbots that understand user intent
Building tools for automated code review or generation
Adding retrieval and reasoning capabilities to existing apps
LangChain’s biggest strength, its flexibility, can also make it a bit tricky to manage. It’s powerful but not always plug-and-play. For smaller teams, setting it up and keeping everything running smoothly might take some extra time and fine-tuning.
LlamaIndex (formerly known as GPT Index) is another open-source orchestration AI framework that helps developers connect LLMs with their own data sources. It’s especially useful for building retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems, where an LLM pulls accurate information from documents, databases, or web pages before generating a response. Core features:
Distributed querying: Efficiently routes and optimizes queries across multiple data sources.
Efficient indexing: Creates searchable structures that improve retrieval speed and accuracy.
LlamaIndex works well for internal knowledge assistants, enterprise chatbots, and analytics tools that rely on company-specific data. You may use LlamaIndex to:
Enable chatbots to access and summarize internal documents or research papers
Turn unstructured files (PDFs, web pages, legal documents) into searchable data
Combine structured and unstructured data for richer insights
LlamaIndex specializes in text-focused tasks. Its performance depends heavily on the quality of embeddings and the input data. Teams using it should ensure they have solid data-cleaning and vectorization processes in place.
Haystack is an open-source AI framework for building question-answering systems, semantic search engines, and document analysis tools. It connects large language models with vector databases, APIs, and data pipelines, making it a versatile option for both prototype and production setups.
The AI framework supports integrations with OpenAI, Hugging Face, and other LLM providers. It also includes Haystack REST API, which allows teams to deploy AI-driven systems as APIs accessible via web or mobile applications. Organizations use Haystack to power document search, internal Q&A systems, and automated content summarization tools. Haystack’s a solid choice when you want to:
Build custom search or FAQ systems
Create document-based question-answering tools
Extract and summarize data from large text collections
Scalability is Haystack’s main challenge. As your data volume grows, maintaining performance and response quality may require additional optimization or infrastructure tuning.
Each tool has its own strengths, but all share the same goal: making large language models usable, scalable, and effective in real-world applications.
Open-source AI frameworks aren’t your only option. If you’d rather skip setup and get enterprise-grade AI tools that work right out of the box, there are all-in-one platforms ready to go, you just choose a plan and start building. These platforms combine pre-trained models, hosting, and data infrastructure so your team can focus on digital transformation results instead of maintenance.
Below, we highlight the most capable and widely used enterprise AI toolkits available today.
Hugging Face goes far beyond a typical AI framework, it’s a complete playground powered by an active global community. The platform provides access to models, datasets, and collaborative workspaces (“Spaces”) that make it easy to create, fine-tune, and deploy ML applications.
The Transformers library by Hugging Face is one of the most popular open-source resources for working with pretrained NLP models. Developers use it for tasks like text classification, summarization, translation, and content generation. Over 50,000 organizations use the platform, including Grammarly, Microsoft, and Meta. You can use Hugging Face to:
Handle text analysis, sentiment detection, and translation
Fine-tune transformer models for your business data
Develop chatbots, copilots, and virtual assistants
Generate content (articles, reports, product descriptions)
Categorize and label large volumes of text
Deploy entire AI systems through managed hosting
Even though Hugging Face has tons of models and tools, it can feel overwhelming at first. Some advanced features and private hubs also come with a price tag, so teams need to plan their budget and setup carefully.
WatsonX, developed by IBM, is a complete suite of AI and machine learning services. It combines a model development studio, a scalable data store, and enterprise-grade governance tools, all built on IBM Cloud.
The platform supports a range of use cases, including natural language processing, computer vision, and predictive analytics. WatsonX is popular among midsize and large enterprises. Companies like NatWest, Samsung SDS, Deloitte, and Eviden rely on IBM’s AI tools to handle data-intensive and compliance-heavy operations. WatsonX is a great fit when you want to:
Conduct medical research and diagnostic analysis
Build enterprise chatbots and virtual assistants
Analyze and extract insights from unstructured data
Detect financial fraud and assess risks
Support decision-making with explainable AI models
WatsonX shines in big, data-heavy organizations, but it can feel like overkill for smaller projects. It also ties you closely to IBM’s cloud ecosystem, which may limit flexibility if you’re using other platforms.
Amazon SageMaker is AWS’s managed machine learning platform that supports everything from data preparation to deployment. It’s designed to make model development faster and easier, even for teams without deep ML expertise.
You can train models, automate ML workflows, and generate real-time predictions directly in the AWS cloud. The platform also scales easily, letting teams handle massive datasets without managing hardware. Data scientists, AI engineers, and analysts use it to accelerate AI adoption in fields like finance, retail, and cloud-based product development — a key focus in current SaaS trends. Companies including Workday, Salesforce, Wix, and Canva use SageMaker to build and manage large-scale ML systems. You may use SageMaker to:
Build, train, and deploy ML models with minimal coding
Automate ML pipelines and prediction generation
Integrate AI functionality into existing AWS-based products
Detect fraud in real time or forecast business outcomes
SageMaker is powerful but not lightweight. Costs can rise quickly with large workloads, and it works best if your team already knows their way around AWS.
OpenAI is the team behind the GPT family of models, ChatGPT, and DALL·E. Their work has defined the current era of generative AI innovation. OpenAI provides accessible APIs that allow developers and businesses to integrate advanced AI into their products with minimal setup.
The OpenAI API (originally built on GPT-4 and now supporting newer models) can power chatbots, recommendation systems, search tools, and analytics platforms. Meanwhile, ChatGPT Plus and ChatGPT Team/Enterprise subscriptions give users direct access to OpenAI’s models with enterprise security and collaboration features. Over 4 million developers, 92% of Fortune 500 companies, and 800 million users rely on OpenAI’s technologies. Brands like Duolingo, Stripe, and Wix use OpenAI to automate workflows, personalize learning, and enhance customer experience. Here’s what you can do with OpenAI tools:
Build chatbots, copilots, and customer assistants
Generate text, images, and audio
Translate or summarize large datasets
Extract insights from unstructured corporate data
Automate repetitive business tasks with AI reasoning
OpenAI’s APIs are easy to plug in but offer limited customization compared to open-source tools. You also rely on external hosting, so data privacy and cost scaling can be concerns for some businesses.
Choosing the right AI framework is about matching your business goals, technical resources, and growth plans with the right set of tools. Here’s how our AI development team typically approaches this decision during the project discovery phase:
Define your business challenge clearly. We start by understanding what you want to achieve with AI: automation, recommendations, analytics, or a custom assistant. The clearer your problem, the easier it is to identify which AI framework fits best.
Map your data and infrastructure. The AI framework must integrate seamlessly with your current tech stack and data format. For example, a SaaS platform already hosted on AWS may benefit more from SageMaker, while a Python-heavy R&D team might prefer PyTorch or JAX.
Evaluate scalability and lifecycle. Some frameworks (like TensorFlow or SageMaker) are built for scaling enterprise systems. Others (like scikit-learn or Keras) are better for experimentation and smaller teams and MVP development. We assess how your AI workload will evolve and plan for growth from day one.
Prototype and benchmark. We often test two or three AI frameworks on a small dataset to compare training speed, resource usage, and accuracy. It’s a simple way to turn theory into proof before you commit.
Plan for maintenance and ecosystem longevity. Active community support and regular updates are crucial. That’s why frameworks like PyTorch, LangChain, and Hugging Face remain top picks — they evolve fast and have strong developer ecosystems.
If you’re not sure where to start, consulting an AI app development provider can help. They’ll assess your architecture, estimate implementation costs, and recommend AI frameworks aligned with your goals.
| Framework / Toolkit | Type | Best For | Key Strengths | Main Limitations |
| TensorFlow | Deep learning | Scalable enterprise AI and cross-platform deployment | Mature ecosystem, production-ready, hardware-optimized | Steeper learning curve, complex setup |
| PyTorch | Deep learning | Research, fast prototyping, and model experimentation | Dynamic graph, flexibility, strong R&D community | Fewer enterprise integrations |
| Keras | Deep learning | Quick prototyping and education | User-friendly API, rapid model iteration | Limited flexibility for advanced use cases |
| JAX | Deep learning | Research and optimization-heavy workloads | High performance, auto-differentiation, GPU/TPU speed | Smaller ecosystem, less production-ready |
| scikit-learn | Machine learning | Predictive analytics and classical ML | Simplicity, strong data processing tools | Not suited for deep learning or large data |
| LangChain | LLM orchestration | Multi-step reasoning, agents, and assistants | Powerful chaining logic, cloud integrations | Complexity in setup and maintenance |
| LlamaIndex | LLM orchestration | Data-driven RAG systems | Efficient data indexing and querying | Quality depends on data embeddings |
| Haystack | LLM orchestration | Search and Q&A systems | Strong document retrieval, flexible APIs | Limited scalability for large datasets |
| AWS SageMaker | Enterprise toolkit | Full ML lifecycle in AWS environment | Scalable, automated workflows, monitoring | Cost and AWS dependency |
| IBM WatsonX | Enterprise toolkit | Governed AI in finance, healthcare | Transparency, explainability, compliance | Smaller community, vendor lock-in |
| Hugging Face | Enterprise / open platform | NLP, content generation, and LLM fine-tuning | Huge model hub, enterprise security options | Paid tiers for advanced usage |
| OpenAI Tools | Enterprise / API platform | Generative AI and automation | State-of-the-art LLMs, simple API integration | Subscription costs, limited customization |
If you’re building from scratch or need model control, start with PyTorch or TensorFlow.
For language-heavy applications like chatbots or copilots, use LangChain or LlamaIndex.
For enterprises scaling AI across teams, go with AWS SageMaker, Azure AI Studio, or WatsonX.
And if your goal is content generation or NLP, nothing beats Hugging Face or OpenAI APIs.
No single AI framework fits every project, but with the right mix of tools, you can turn your AI idea into a scalable, real-world solution.
Choosing an AI framework can be challenging. With new tools and libraries appearing constantly, it’s easy to feel lost, yet this choice directly affects your product’s speed, cost, and long-term scalability.
The right framework helps you validate ideas faster, integrate AI smoothly, and grow without major rework. The wrong one can limit flexibility, create technical debt, or slow your progress.
That’s why AI framework selection should start early, backed by clear business goals and technical evaluation. In a fast-changing AI market, quick testing and informed decisions are key. Pick the framework that fits your product and team, and you’ll move from idea to impact much faster.
